Withania Somnifera
July 2020
Withania somnifera: Nature’s boon to mankind
Withania somnifera is a miraculous herb that is a nature’s gift to mankind. Withania is having excellent medicinal properties and can serve as a remedy for several health conditions. Traditionally, in Sanskrit, Withania somnifera is known as Ashwagandha or “smell like a horse”. This unique name was attributed to the herb considering the smell of the roots, which is similar to the smell of a horse. Scientifically, according to the Linnaeus classification, the plant is known as Withania somnifera (L.)Dunal. The name “Dunal” was attributed to the popular French botanist Michel Félix Dunal. The use of Ashwagandha is dated back to centuries in Ayurveda and Unani medicine. Ayurvedic scriptures documented abundant use of the plant for general wellbeing and in ailments. Similarly, in Unani medicine, recommendation of this herb is recorded in the book “Kitab-ul-Hashaish” during Dioscorides (78 AD).
Ashwagandha (Withania somnifera)
Ashwagandha (Withania somnifera) is a perennial shrub and is known as Indian ginseng, and winter cherry. The herb belongs to the nightshade or Solanaceae family. Traditionally, Withania somnifera root extract is used for the medication and as a supplement. Generally, consumption of the Withania root extract in a capsule or powder form is advised with milk or water. The herb is generally abundant in the drylands of India and the African region. It is also found in other Asia Pacific countries. For thousands of years, this herb is serving as the premier source of medicine in Ayurveda. The herb received enormous consideration due to the benefits it renders to human health. Taxonomically, the plant belongs to the clade Angiosperms, Eudicots, Asterids, and the order is Solanales, family Solanaceae, genus Withania, and species somnifera. The plant grows between 15 and 30 inches and bell-shaped green flower, and orange fruits are its phenotypical characteristics.
Digest: Withania plant
* Small ~30 inch plant of Solanaceae or the nightshade family.
* Having bell shaped green flower and orange fruit.
* Grows in the drylands of Western India or Northern African region abundantly.
* Scientifically, in the binomial nomenclature of the plant honored French botany Prof. Michel Félix Dunal. and the plant is named as Withania somnifera (L.) Dunal.
The plant is also known as Ashwagandha, winter cherry, and Indian ginseng.
Withania somnifera benefits
Numerous health benefits can be received through the consumption of Withania in a different form, especially the root extract. The presence of several phenolic compounds, lactone triterpenoids, especially withanolides, has a considerable role in the health benefits.
- Energy inducer: Withania somnifera is having scientifically proven health benefits and is known to boost the energy in improving the metabolism of a person. Traditionally, Withania somnifera is known as “Rasayana”, meaning a rejuvenator or a herb that does energy replenishment [1].
- Homeostatic effect: Withania is known to have a homeostatic effect[2] on the human body, i.e., it can balance the constituents and elements of the human body, and often it can boost up certain physiological requirements if it is low and vice versa. For instance, for people with low libido[3], Ashwagandha serves as a libido booster. It can boost overall metabolism[4, 5, 6] for people who are in dearth of energy. On the contrary, Withania can reduce blood sugar and balance it for better health.
- Managing stress and anxiety: Stress and anxiety are part of modern life. Solutions are being searched in contemporary medication, exercise, cognitive behavior therapy (CBT), and many other therapeutic approaches. However, none of these approaches have been proved completely effective or remedial so far. Withania sominfera root extract benefits extremely well in countering regular stress and anxiety. Scientific evidence suggests excellent outcomes in this regard. Besides, the Withania supplement was found to be beneficial in acute and chronic insomnia as well [7]. Clinical evaluation with different anxiety and stress scales such as Hamilton Anxiety Scale (HAM-A), Beck Anxiety Inventory (BAI) proved the benefits of regular Withania supplement consumption in managing stress and anxiety [8]. Cortisol is the stress marker that enhances as part of any physiological stress response. Aswagandha displayed remarkable efficacy in reducing cortisol levels not only in humans but also in animals [9].
- Immunomodulation: Our immunity or natural defense system of the body is the gift of nature which improved after thousands of years of evolution. The humoral (B cell-dependent) and the cytotoxic (T cell-based) immunity helps us to combat the uncountable number of pathogens, even many of which we are may not be aware of. Ashwagandha can improve immunity naturally. Some research evidence is present that claim Withania root extract as an excellent immunomodulator and immune booster [10].
- Inflammation reduction and somniferous effect: Pathogenic invasion, cellular damage, and the protective response of the body are reflected through inflammatory responses. Inflammation is represented through the generation of heat and pain in the local area of the tissues, swelling of tissue, discoloration, and redness, and functional loss. Ashwagandha showed an extensive anti-inflammatory benefit for protein denaturation[11]. The scientific name of the herb was derived from the ancient and modern scientific evidence of somniferous of the sleep-inducing effect of the root extract of the herb. Abundant recent scientific evidence is available that proved the significant role of Withania somnifera in sleep induction and improving the quality of sleep [ 12, 13, 14, 15].
- Improving sexual-health: Withania somnifera is a proven libido booster. Research outcome suggests that Withania root extract can help in improving sexual health for both males [16, 17] and females [18]. Most of the other herbal or synthetic compounds can render health benefits to either male or female reproductive issues whereas Withania is having a magical effect on either sex. In males, Ashwagandha improved the testosterone level and improved the semen quality in healthy as well as in infertile males [19, 20].
- Anti-aging effect: Ageing is an inevitable part of human life. Stories, myths, religious texts, and history are having abundant evidence where human beings left no stones unturned to conquer aging. However, so far there is no good news. Ancient science also invested efforts against aging and certain herbs were promising. Withania is one such herb that may stall aging. Scientific exploration showed remarkable results in C. elegans [21]. Probably Withania helps in maintaining the telomere length which is a key factor for aging and allows arresting aging. In humans [22], experiments have shown some results that are required to be expanded before a general conclusion is obtained.
- Memory, alertness, and cognition: Better memory and cognitive ability is a high-quality human trait. Ancient, medieval, modern science attempted to harness benefits from all possible ways to improve memory and cognition. However, ancient Ayurveda concentrated on this important fact and several herbal formulations were recommended. Ashwagandha or Withania somnifera was considered unanimously for the benefit of improving memory and cognitive abilities [23, 24]. Research also proved that Ashwagandha considerably improves alertness, especially after waking up in the morning.
- Cardiorespiratory health and muscle strength: Health is considered as wealth for all of us. Based on personal beliefs, abilities, health conditions, age, and interests we opt for one or the other health-boosting practice that may include yoga, gym, jogging, pilate, different form of martial art, and exercises. Proper nutrition and supplement are essential to maintain and improve health. Withania somnifera root extract consumption as a supplement benefited in managing the vital signs and in enhancing the cardiorespiratory efficiency and muscle growth [25, 26, 27].
- Cholesterol and lipid level management: Modern lifestyle has given us a technology-led, comfortable ambiance which has become the signature of our civilization. However, such development has been achieved in the expenditure of our health, such as obesity, cardiovascular problems, and other health issues. Withania has a considerable cholesterol-lowering effect and can benefit in reducing Low-density lipoprotein (LDL) and triglycerides, and augmenting the level of High-density lipoprotein (HDL) [27].
- Eliciting the antioxidant profile and reducing oxidative stress: Oxidative stress is harmful to the body as it produces many reactive species and free radicals that damage the cells and organelles. Scavenging of such free radicals is necessary, preferably in a natural way to protect the elementary level damage of the cellular construct. Interesting relation has been established between oxidative stress and antioxidant level. Improved antioxidant profile aids in countering the effect of the outcomes of the oxidative stress and lipid peroxidation[28, 29].
- Other benefits: Apart from these benefits for healthy human beings and common health issues, Withania is specifically efficacious and precise in improving several disease conditions that can range from cancer to complex neurological conditions.
Digest: Herb Benefits
Up regulation
In modern experiments, it has been proven that Ashwagandha is an amazing modulator of multiple biochemical and physiological parameters. It does so in a synchronized fashion that attributed this herb as the best “Rasayana”, and a miraculous medicinal plant. The evidence available till now suggest that Withania somnifera can induce testosterone level in male, enhances the strength, increases the immunity, anaerobic exercise capacity or cardiorespiratory outputs, augments the luteinizing hormones in women, improves motivation, elevates mood and social functioning in general, significantly increases overall wellbeing, improves alertness, enhances the antioxidant level, cognition, dieresis, motor control, improves the activity of the natural killer cells, surges mental processing, enhances general quality of life, improves certain WBC cells types, and many other biochemical and physiological factors.
Down regulation
On the contrary, the herb is having the potential to reduce the number of factors that include several symptoms of diseases, serum albumin, reaction time, pain sensation, muscle damage, lipid peroxidation, insomnia, fat deposition, inflammation and irritability, C-reactive proteins, weight, LDL, Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), fatigue, depression, blood glucose, total cholesterol, stress, and anxiety.
These many positive outcomes are rarely achieved by other natural supplements, herbs, and medicines. Moreover, Ashwagandha is known to be generally safe to use since ancient times, at it could be used with a varying range of dosages. So far, the observed side-effects are limited, and severe adverse effects are almost none. Therefore, this time-tested medicinal plant could be our elixir and can have an application in health and wellness in a multipurpose way.
Consumption of Ashwagandha
The consumption of Ashwagandha predominantly considers the root extract from ancient times. Most of the time, as single or part of a polyformulation, Ashwagandha is consumed with water or milk only to harness the maximum benefit. The roots are dried and ground into powder form for consumption. In modern times, capsules or tablets use such dried yellow powder of the roots as the active ingredient.
What is the secret ingredient?
We have discussed the immense benefits of this plant. The question arises, what is the secret ingredient? How does this herb become so effective? Scientific investigations suggest that the phytochemicals present in the herb made it so.
What is a phytochemical?
As part of plant metabolism, especially secondary metabolism, several large and complex ring structured chemical compounds are naturally produced by the plant. Those are known as phytochemicals. The purpose of these chemicals as a byproduct of the plant is often used for the plant’s defense from harmful animals including insects, predators, and others. Phytochemicals are helpful for human health, growth, and defense against disease conditions and are used as an effective medication. However, essentially not all phytochemicals are beneficial; harmful phytochemicals are known as phytotoxins that have a toxic effect on humans and other animals. However, the purpose of the plant to produce the phytochemical is almost the same, to save itself from outside harmful impact.
Phytochemicals present in Withania
Research outcomes suggest that Withania is having many phytochemicals that are produced as the byproduct of the plant’s secondary metabolism. An array of ~40,000 different chemical molecules is present in Withania. An optimum level of phytochemical production in the plant depends on the environmental stress, soil conditions such as soil moisture stress [30]. The root extract of the plant contains a range of alkaloids and steroidal lactones. Chemical constituent analysis of those alkaloids and steroid lactones suggested most of them are Withanine, somnine, anahydrine, withananine, pseudo-withanine tropane, somniferine, pseudo-tropine, choline, somniferinine, anaferine, and isopelletierine [31]. The most important components present are various types of Withanolide and Withaferrin as shown in Figure 1.
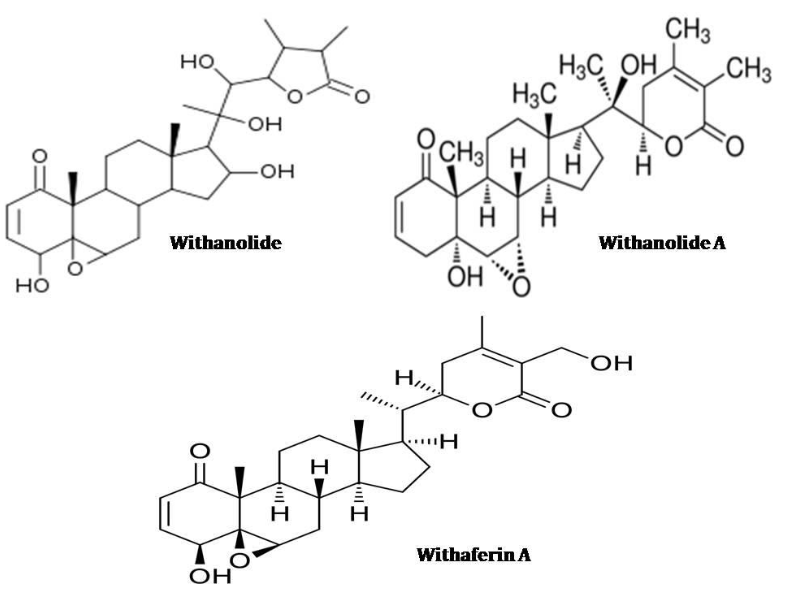
Digest: Phytochemicals
* Phytochemicals serve as the secret ingredient for the medicinal properties or as active pharmaceutical ingredients (API).
* There are more than 40,000 compounds found in Withania.
* Phytochemicals are mostly alkaloids and lactones structurally.
* Major compound in Withanolide, Withanolide A, and Withaferin.
References
- Singh N, Bhalla M, de Jager P, Gilca M. An overview on ashwagandha: A Rasayana (Rejuvenator) of Ayurveda. African Journal of Traditional, Complementary and Alternative Medicines. 2011;8(5S).
- Ahmad M, Dar NJ. Withania somnifera: Ethnobotany, Pharmacology, and Therapeutic Functions. InSustained Energy for Enhanced Human Functions and Activity 2017 Jan 1 (pp. 137-154). Academic Press.
- Mamidi P, Thakar AB. Efficacy of Ashwagandha (Withania somnifera Dunal. Linn.) in the management of psychogenic erectile dysfunction. Ayu. 2011 Jul;32(3):322.
- Baliga MS, Shivashankara AR, Meera S, Palatty PL, Haniadka R, Arora R. The Health Benefits of the Ayurvedic Anti-Aging Drugs (Rasayanas): An Evidence-Based Revisit. Bioactive Food as Dietary Interventions for the Aging Population: Bioactive Foods in Chronic Disease States. 2012 Oct 22:209.
- Sangwan RS. Withanomics of Ashwagandha: the specialized metabolic biology of an ayurvedic herb. Planta Medica. 2012 Mar;78(05):P_17.
- Choudhary D, Bhattacharyya S, Joshi K. Body weight management in adults under chronic stress through treatment with Ashwagandha root extract: a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Journal of evidence-based complementary & alternative medicine. 2017 Jan;22(1):96-106.
- Langade D, Kanchi S, Salve J, Debnath K, Ambegaokar D. Efficacy and safety of Ashwagandha (Withania somnifera) root extract in insomnia and anxiety: a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study. Cureus. 2019 Sep;11(9).
- Pratte MA, Nanavati KB, Young V, Morley CP. An alternative treatment for anxiety: a systematic review of human trial results reported for the Ayurvedic herb ashwagandha (Withania somnifera). The Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine. 2014 Dec 1;20(12):901-8.
- Salve J, Pate S, Debnath K, Langade D. Adaptogenic and Anxiolytic Effects of Ashwagandha Root Extract in Healthy Adults: A Double-blind, Randomized, Placebo-controlled Clinical Study. Cureus. 2019 Dec;11(12).
- Bhat H, Sampath P, Pai R, Bollor R, Baliga M, Fayad R. Indian medicinal plants as immunomodulators: scientific validation of the ethnomedicinal beliefs. Bioactive Food as Dietary Interventions for Arthritis and Related Inflammatory Diseases: Bioactive Food in Chronic Disease States. 2012 Oct 22:215.
- Chandra S, Chatterjee P, Dey P, Bhattacharya S. Evaluation of anti-inflammatory effect of ashwagandha: a preliminary study in vitro. Pharmacognosy Journal. 2012 May 1;4(29):47-9.
- Salve J, Pate S, Debnath K, Langade D. Adaptogenic and Anxiolytic Effects of Ashwagandha Root Extract in Healthy Adults: A Double-blind, Randomized, Placebo-controlled Clinical Study. Cureus. 2019 Dec;11(12).
- Kelgane SB, Salve J, Sampara P, Debnath K. Efficacy and Tolerability of Ashwagandha Root Extract in the Elderly for Improvement of General Well-being and Sleep: A Prospective, Randomized, Double-blind, Placebo-controlled Study. Cureus. 2020 Feb;12(2).
- Candelario M, Cuellar E, Reyes-Ruiz JM, Darabedian N, Feimeng Z, Miledi R, Russo-Neustadt A, Limon A. Direct evidence for GABAergic activity of Withania somnifera on mammalian ionotropic GABAA and GABAρ receptors. Journal of ethnopharmacology. 2015 Aug 2;171:264-72.
- Langade D, Kanchi S, Salve J, Debnath K, Ambegaokar D. Efficacy and safety of Ashwagandha (Withania somnifera) root extract in insomnia and anxiety: a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study. Cureus. 2019 Sep;11(9).
- Sengupta P, Agarwal A, Pogrebetskaya M, Roychoudhury S, Durairajanayagam D, Henkel R. Role of Withania somnifera (Ashwagandha) in the management of male infertility. Reproductive biomedicine online. 2018 Mar 1;36(3):311-26.
- Nasimi Doost Azgomi R, Zomorrodi A, Nazemyieh H, Fazljou SM, Sadeghi Bazargani H, Nejatbakhsh F, Moini Jazani A, Ahmadi AsrBadr Y. Effects of Withania somnifera on reproductive system: A systematic review of the available evidence. BioMed research international. 2018 Jan 24;2018.
- Dongre S, Langade D, Bhattacharyya S. Efficacy and safety of Ashwagandha (Withania somnifera) root extract in improving sexual function in women: a pilot study. BioMed research international. 2015 Jan 1;2015.
- Mahdi AA, Shukla KK, Ahmad MK, Rajender S, Shankhwar SN, Singh V, Dalela D. Withania somnifera improves semen quality in stress-related male fertility. Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine. 2011 Jan 1;2011.
- Ahmad MK, Mahdi AA, Shukla KK, Islam N, Rajender S, Madhukar D, Shankhwar SN, Ahmad S. Withania somnifera improves semen quality by regulating reproductive hormone levels and oxidative stress in seminal plasma of infertile males. Fertility and sterility. 2010 Aug 1;94(3):989-96.
- Kumar R, Gupta K, Saharia K, Pradhan D, Subramaniam JR. Withania somnifera root extract extends lifespan of Caenorhabditis elegans. Annals of neurosciences. 2013 Jan;20(1):13.
- Lopresti AL, Drummond PD, Smith SJ. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover study examining the hormonal and vitality effects of ashwagandha (Withania somnifera) in aging, overweight males. American journal of men’s health. 2019 Mar;13(2):1557988319835985.
- Choudhary D, Bhattacharyya S, Bose S. Efficacy and safety of Ashwagandha (Withania somnifera (L.) Dunal) root extract in improving memory and cognitive functions. Journal of Dietary Supplements. 2017 Nov 2;14(6):599-612.
- Alzoubi KH, Al Hilo AS, Al-Balas QA, El-Salem K, El-Elimat T, Alali FQ. Withania somnifera root powder protects againist post-traumatic stress disorder-induced memory impairment. Molecular Biology Reports. 2019 Oct 1;46(5):4709-15.
- Choudhary B, Shetty A, Langade DG. Efficacy of Ashwagandha (Withania somnifera [L.] Dunal) in improving cardiorespiratory endurance in healthy athletic adults. Ayu. 2015 Jan;36(1):63.
- Wankhede S, Langade D, Joshi K, Sinha SR, Bhattacharyya S. Examining the effect of Withania somnifera supplementation on muscle strength and recovery: a randomized controlled trial. Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition. 2015 Dec 1;12(1):43.
- Raut AA, Rege NN, Tadvi FM, Solanki PV, Kene KR, Shirolkar SG, Pandey SN, Vaidya RA, Vaidya AB. Exploratory study to evaluate tolerability, safety, and activity of Ashwagandha (Withania somnifera) in healthy volunteers. Journal of Ayurveda and integrative medicine. 2012 Jul;3(3):111.
- Gupta SK, Dua A, Vohra BP. Withania somnifera (Ashwagandha) attenuates antioxidant defense in aged spinal cord and inhibits copper induced lipid peroxidation and protein oxidative modifications. Drug metabolism and drug interactions. 2003;19(3):211-22.
- Palash M, Mitali G, Kumar MT, Prasad DA. Pharmacognostic and free-radical scavenging activity in the different part of ashwagandhaWithania somnifera (L. Dunal). Int J Drug Dev Res. 2010;2:830-43.
- Shah S, Saravanan R, Gajbhiye NA. Phytochemical and physiological changes in Ashwagandha (Withania somnifera Dunal) under soil moisture stress. Brazilian Journal of Plant Physiology. 2010;22(4):255-61.
- Bara JK, Soni R, Jaiswal S, Saksena P. Phytochemical study of the plant Withania somnifera against various diseases. Bara JK, Soni R, Jaiswal S, Saksena P. Phytochemical study of the plant Withania somnifera against various diseases. IOSR Journal of Agriculture and Veterinary Science (IOSR-JAVS) e-ISSN: 2319-2380, p-ISSN: 2319-2372. Volume 9, Issue 8 Ver. II (Aug. 2016), PP 109-112.